

Each correctly chosen pattern counts for one point, resulting in a total scale score ranging from 0 to 24. The respondent has to choose which of the six alternatives fits best. On the bottom of the page six patterns are printed, one of which fits in the missing section. Each subset contains 12 items, and each item consists of a drawing (matrix) of a pattern from which a section is missing. The original version of the RCPM consists of three sections, A, Ab, and B. The RCPM is a non-verbal visual test, assessing the ability for non-verbal and abstract reasoning. Fluid intelligence is assessed with the Raven Coloured Progressive Matrices (RCPM, Raven, 1995). Contrary to crystallized intelligence, fluid intelligence is particularly vulnerable to decline associated with aging (Horn, 1985 Smits, Smit, Van den Heuvel, & Jonker, 1997). Brain, published online Decemdoi: 10.Fluid intelligence is defined as the ability to deal with new information. Graph lesion-deficit mapping of fluid intelligence. “More attention to lesion studies is essential to uncover the relationship between the brain and cognition, which often determines how neurological disorders are treated.” “Our approach of combining novel lesion-deficit mapping with detailed investigation of APM performance in a large sample of patients provides crucial information about the neural basis of fluid intelligence.” “This supports the use of APM in a clinical setting, as a way of assessing fluid intelligence and identifying right frontal lobe dysfunction.” “Our findings indicate for the first time that the right frontal regions of the brain are critical to the high-level functions involved in fluid intelligence, such as problem solving and reasoning,” Professor Cipolotti said.

They found that fluid intelligence impaired performance was largely confined to patients with right frontal lesions - rather than a wide set of regions distributed across the brain. This enabled the authors to disentangle the brain map of cognitive abilities from the patterns of damage - allowing them to map the different parts of the brain and determine which patients did worse in the fluid intelligence task according to their injuries. Their approach treated the relations between brain regions as a mathematical network whose connections describe the tendency of regions to be affected together, either because of the disease process or in reflection of common cognitive ability. The researchers then introduced a novel ‘lesion-deficit mapping’ approach to disentangle the intricate anatomical patterns of common forms of brain injury, such as stroke. The test contains multiple choice visual pattern problems of increasing difficulty.Įach problem presents an incomplete pattern of geometric figures and requires selection of the missing piece from a set of multiple possible choices. In the new study, University College London’s Professor Lisa Cipolotti and colleagues investigated 227 patients who had suffered either a brain tumor or stroke to specific parts of the brain, using the Raven Advanced Progressive Matrices (APM): the best-established test of fluid intelligence. Such ‘lesion-deficit mapping’ studies are difficult to conduct owing to the challenge of identifying and testing patients with focal brain injury.Ĭonsequently, previous studies have mainly used functional imaging (fMRI) techniques - which can be misleading. To establish which parts of the brain are necessary for a certain ability, researchers must study patients in whom that part is either missing or damaged. It is thought to be a key mental capacity involved in ‘active thinking,’ fluid intelligence declines dramatically in various types of dementia and reflects the degree of executive impairment in older patients with frontal involvement.ĭespite the importance of fluid intelligence in defining human behavior, it remains contentious whether this is a single or a cluster of cognitive abilities and the nature of its relationship with the brain.
Fluid intelligence consists of professional#
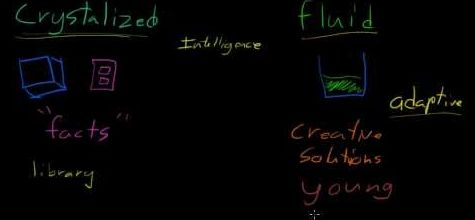
memory), and predicts educational and professional success, social mobility, health and longevity. It ranks amongst the most important features of cognition, correlates with many cognitive abilities (e.g. Image credit: Cipolotti et al., doi: 10.1093/brain/awac304.įluid intelligence refers to the ability to solve challenging novel problems when prior learning or accumulated experience are of limited use.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
